01- Alphabet, Numbers, & Symbols
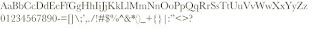
02- John Baskerville (1706-1775) designed the Baskerville typeface.
03- The Baskerville typeface was designed in 1757.
04- Baskerville is classified as a transitional typeface.
05- Transitional typefaces evolved form the typefaces used in the 16th and 17th centuries. Typefaces in this category are beautifully suited from the text because of their regularity and precision. The axis of the round characters is vertical or less inclined than earlier faces, the s is slightly pronounced, and serifs are thin, flat, and bracketed. These typefaces also have a slightly pronounced contrast between hairlines and the main strokes, and have a flat or triangular tip where diagonal strokes meet (e.g., at the base of a W).
06- Three transitional fonts are ITC New Baskerville, Olympian STD, and Bookman STD.
07- 1757—
January 2 British troops occupy Calcutta India
January 5 Failed assassination attempt on French king Louis XV by Damiens
January 17 German Diet declares war on Prussia
March 17 Prince Mas Said of Mataram surrenders to Mangkubumi in Java
April 6 English king George II fires minister William Pitt, Sr.
May 1 Austria and France divide Prussia
May 6 Battle at Prague: Frederik II of Prussia beats emperor army
June 18 Battle at Kolin Bohemia: Austrian army beats Prussia
June 23 Robert Clive defeats Indians at Plassey, wins control of Bengal
July 26 Battle at Hastenbeck: French army beats duke of Cumberland
August 9 English Ft. William Henry, New York, surrenders to French and Indians troops
August 30 Battle at Gross Jagerndorf: Russian army beats Prussia
October 16 Austrian troops occupy Berlin
November 5 Battle at Rossbach (7 year war/French and Indian War)
December 5 Battle at Leuthen: Prussian army beats Austrians
08- John Baskerville, TS Baskerville, Baskerville No. 2, Baskerville, TS Old Baskerville, ITC New Baskerville
09- John Baskerville was born in 1706 at Wolverley in Worcestershire. He was a man with a lifelong passion for beautiful lettering and books. By 1723 he had become a skilled engraver of tombstones and was teaching writing. He moved to Birmingham in about 1726 and set up a school in the Bull Ring where he taught writing and book-keeping, whilst still maintaining his work as an engraver. In 1738 he set up a japanning business in Moor Street (japanning was an early form of enameling, in which he first showed his mettle as an innovator, ‘effecting an entire revolution’ in the manufacture of japanned goods, and specializing in salvers, tea trays, bread baskets and the like. Within a decade he had become a wealthy man and had bought an estate of some eight acres and a large house on the site of the present-day Baskerville House.
Whilst keeping on his japanning business, in about 1750 he once again turned his attention to his passion, typography. He experimented with paper-making, ink manufacturing, type founding and printing, producing his first typeface in about 1754. Never afraid to innovate, he made changes to the way in which metal type was made, enabling him to produce finer, more delicate lettering than any before him had achieved. He invented his own lustrous, uniquely black, opaque ink; he was the first to exploit commercially James Whatman’s invention of wove paper, which was much smoother than the traditional laid paper; and he modified the printing process by using heated copper cylinders to dry the ink before it had time to soak too far into the paper. All of these innovations enabled Baskerville to produce printed work of an elegance, crispness and clarity never seen before.
In 1757 he published his first book, an edition of Virgil. This was followed by some fifty other classics. In 1758 he became printer to the Cambridge University Press for which, in 1763, he published his masterpiece. Ironically for a confirmed atheist, his greatest work was a folio edition of the Bible, which represented a monumental advance upon the standards and practices of the time. He established a lasting friendship with the American scientist and statesman Benjamin Franklin, who had built up a successful printing business in Philadelphia, and who visited Baskerville in Birmingham.
John Baskerville’s guiding principles in his work were simplicity, elegance and above all, clarity. The typeface that bears his name remains one of the most pleasing of the all-time great classical fonts, vastly superior to the dismal Times Roman, which sadly, has become all too ubiquitous. (If you're lucky enough to have John Baskerville's font installed on your computer, you will be reading it right now.)
John Baskerville was a friend of the Boulton family, and a good friend and mentor to the young Matthew Boulton as he was growing up. Defying convention, he lived openly with his partner, Sarah Eaves, whose husband had deserted her; rejected religion, pouring withering scorn upon religious bigots; and indulged his fondness for show, wearing masses of gold lace and riding about in a lavishly decorated carriage (see right hand panel).
John Baskerville died in 1775 and was buried in a little mausoleum in his garden. Aris’ newspaper carried this news on 23rd January.1775 – "Died. On Monday last, at Easy Hill in this Town, Mr John Baskerville; whose memory will be perpetuated, by the Beauty and Elegance of his Printing, which he carried to a very great Perfection."
Baskerville died in January 1775 at the age of sixty-nine. He was followed thirteen years later by his partner Sarah and they left no heirs. It was left to an American to discover the genius behind the designs that he had spent so many years perfecting. His personal crusade was finally won when he was recognized, albeit posthumously as one of the greatest type designers that ever lived. It was a fitting memorial to a great man whose typeface is still in use today. Renowned for his attention to detail and his tenacity in the face of obstacles, one would suppose that when he was finally laid to rest in a mausoleum in his own grounds, as requested, with a seemingly proper appreciation at last of his life’s work, he would finally find rest, with nothing left to strive for. However, as far as John Baskerville was concerned, even in death he was destined to be unsettled with where he was put.
After Sarah followed him to the grave on 21st March 1788 Baskerville’s house was sold to John Ryland who then moved in 1791 after it was attacked and wrecked during the Birmingham Riots. On his death Ryland left the house to his son, Samuel. Samuel demised it to Thomas Gibson who cut a canal through the grounds and converted the rest of the property into wharf land. Unfortunately the intended route for this canal lay directly through the mausoleum and the decision was made to demolish the building to make way for it. The body, however, lay undisturbed beneath. Later on though, in 1821, the lead coffin was discovered by workmen digging for gravel and a few days later it was disinterred.
Nobody came to claim the coffin and contents and because of Baskerville’s atheism he could not be interred in Holy ground in the local cemetery. For want of somewhere to put them, the coffin and its contents were deposited in Messrs. Gibson & Sons warehouse in Cambridge Street (it seems ironic that Baskerville should be stored on a street bearing the same name as the university for whom he was Master Printer for ten years). According to writings by Langford: "a few individuals were allowed to inspect it. The body was in a singular state of preservation, considering that it had been underground about 46 years. It was wrapt in a linen shroud… The skin on the face was dry but perfect. The eyes were gone, but the eyebrows, eyelashes, lips and teeth remained. The skin on the abdomen and body generally was in the same state with that of the face. An exceedingly offensive effluvia, strongly resembling decayed cheese, arose from the body and rendered it necessary to close the coffin in a short time".
The coffin was left in Gibson’s warehouse for the next eight years and there are quotes recorded from someone who lived next door to the warehouse. The neighbour alleges that Gibson used to charge 6d a head "to see the body… and as a child I saw the coffin reared up on end in Gibsons…" After this it was transferred to the shop of John Marston, a plumber and glazier. The coffin was again reopened and a local artist, Thomas Underwood, made a pencil sketch of the body. Unfortunately this second opening of the coffin was to prove a disaster to the preservation of the body. Mrs Marston spoke of the body being "mummified, looking but very little changed but soon changing much." There were many reports of people seeing the body then becoming ill and Marston was anxious to be rid of it. Marston applied to put the body in his own family vault at St Philip’s church, but permission was refused.
Desperate to be rid of the body, Marston spoke of his problem to a visiting book-seller, Mr Nott. Mr Nott of course knew exactly who Baskerville was and as a book-seller perhaps better appreciated what he had done for the printed page. He said that he would be honoured if Baskerville’s remains could be placed in his family vault at Christ Church if they could work out a way to get them there. Fortunately Marston had a useful contact in a Mr Barker who was not only an intimate friend but was also a Church Warden of Christ Church. Seeing a way out of his predicament Marston immediately put his case to his friend who agreed that the situation was untenable and something must be done "indeed, I keep the keys and at such time of the day they are on the hall table." Quick to take a hint, Marston called at Mr Barker’s house to find that when the butler opened the door the keys were indeed on the hall table. The butler informed him that Mr Barker was not at home and turning round, left the room leaving Marston in the hall. Marston quickly took the keys and with the aid of a hand barrow covered with a green baize cloth, moved the body to a place in Mr Nott's vault. A notice was then inserted in a Birmingham paper that Baskerville’s body had been buried between two pools near Netherton, beyond Dudley.
In 1892 a man called Talbot Baines Reed said in a letter that the mystery of Baskerville’s whereabouts ought to be solved as not everybody believed the notice. A check by churchwardens and others revealed that the last vault was indeed full and they discovered Baskerville’s lead coffin with his name on it in his own type behind a double layer of brick-work instead of the usual stone tablet. The coffin was opened, inspected and then quickly reinterred and cemented in. A plaque bearing the words ‘In these catacombs rest the remains of John Baskerville, the famous Printer’ was placed on the outside of the church.
However, in 1890 the church was demolished to make way for shops and administrative buildings. A few years ago these too were demolished and a grassy area* with a walk, and a flight of steps called Christ Church Passage is all that now remains. The bodies in the vaults were removed and Baskerville’s body was reinterred in the Church of England cemetery in Warstone Lane in a vault under the chapel. For an atheist, poor Baskerville seemed to be coming acquainted with a variety of holy places. The tablet was placed at the entrance to the vault but eventually this chapel too was demolished and the entrance blocked up to deter vandals. The tablet is now hidden behind the wall.
So this is where Baskerville’s body finally finished its travelling. Perhaps he would have been pleased to know there was no longer a holy building over him. He did not want to be buried in consecrated ground and although a vault is to all intents and purposes consecrated, at least there is no church or chapel standing over him to add insult to injury.
Just as his typeface is now recognized as one of the greatest ever designed, so his body is more or less where he would want it, in a place where there is no church. Perhaps he would have been happy about this as it proves that if you keep persevering, you will eventually get what you want. This was John Baskerville to the letter.
http://bobmiles.bulldoghome.com/pages/bobmiles_bulldoghome_com/morejbask.htm
10- The historian Lord Macaulay on John Baskerville's edition of the Bible: 'It went forth to astonish all the librarians of Europe’








